Lecture 7 - STL
std::sort(ar, ar + size);
std::copy(v.begin(), v.end(), ar); // copy over
std::copy(ar, ar + size, v.begin()); // cpy back
std::vector<int> vec(v.begin(), v.end()); // construct vector from elts in another container
std::vector<int> vec2(size, -1); // fill with -1's
std::swap(T a, T b);
std::max(T a, T b);
Review of Array
Amortized Complexity
Array Class: Complexity of Appending n elements to a full array
steps to copy: O(n)
push_back: each is O(1), n times = O(n)
Amortized: total steps/ total push-backs = (n + n* 1) / n = 2n/n = O(1)
On average, over a whole bunch of push backs, each push back is ~O(1)
STL
C++ features that STL Relies on
- type bool
- const-correctness, const-casts
- namespaces:
- using namespace std;
- using std::vector;
- Templates
- Inline functions
- exception handling
- Implicit Initialization
- Operator Overloading
- Extended syntax for new()
- Keywords explicit and mutable
STL helps minimize use of pointers and dynamic memory allocation
STL sort() is typically best possible big-O complexity, STL prioritized for speed
However, nth_element() and linked lists in STL do not have best possible big-O complexities
STL Containers
- vector<> and deque<>
- stack<> and queue<> are adaptors
- set<> and multi_set<>
- map<> and multi_map<>
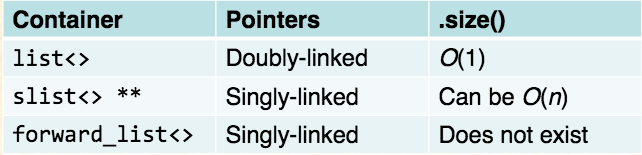
- list<> and array<>
- bit_vector is same as vector<bool>
Copying and Sorting Arrays
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100;
int main() {
vector<int> v(N, -1);
int ar[N];
for (unsigned j = 0; j != N; j++) {
v[j] = (j * j * j) % N;
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), ar); // copy over
copy(ar, ar + N, v.begin()); // copy back
sort(ar, ar + N);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<int> reversed(v.rbegin(), v.rend());
}
}
Using Iterators - implement same algorithm for multiple data structures
template<class InputIterator>
void genPrint(InputIterator begin, InputIterator end) {
auto it = c.begin();
while(begin != end) {
out << *begin++ << " ";
}
} // genPrint
DON'T write a template version without iterators, it will cause compiler errors
// Overload for each container type you need to output
template<class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const vector<T>&c) {
for (auto &x: c)
out << x << " ";
return out;
}
- Implement another version for list<T>, deque<T>, etc.
Utilities and Function Objects
- swap<>, max<>
Functors remove the need for function pointers
Index Sorting
FUNCTOR
class SortByCoord {
const vector<double>& _coords;
public:
SortByCoord(const vector<double>&z) : _coords(z) {}
bool operator()(unsigned i, unsigned j) const {
return _coords[i] < _coords[j];
}
};
USING FUNCTOR
vector<unsigned int> idx(100);
vector<double> xCoord(100);
for(unsigned k = 0; k != 100; k++) {
idx[k] = k;
xCoord[k] = rand() % 1000 / 10.0;
}
SortByCoord sbx(xCoord); // declaration of function object
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(), sbx); // call
Generating Random Permutations - great for testing programs
// write the code for it HERE
Filling a Container with Values - using iota()
// Fill vector perm with values starting at 0
iota(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);
// Fill array starting at 0
iota(perm, perm + N, 0);